How to optimize websites for AI Search – technical requirements

SEO is far from dead, but it’s no longer enough on its own. The search behaviors started to change dynamically after 2022 and the outburst of AI tools, including OpenAI’s ChatGPT, Google Gemini, or Perplexity. A traditional search engine is not always the start of the customer journey. The search for answers, reviews, services, and products starts in the window of the chat more and more often.
Our research, described in the AI in Search & Shopping 2025 report, shows that:
- 77% of consumers use AI tools on a regular basis (monthly or more frequently)
- 96% report frustrations with traditional search engines, primarily excessive ads and irrelevant results
The shift towards AI-powered search is happening very dynamically. And the ways of website optimization shift along with it.
And while there are numerous articles on optimizing website’s content in order to get cited in AI-generated responses, not many of them cover the technical details of optimization.
In this article we focus on answering the question: what technical parameters, configurations, and technology choices best support AI Search Optimization (AISO)? In other words, what should you implement to help large language models (LLMs) – the engines behind tools like ChatGPT, Perplexity, and Gemini – efficiently process your website and select it as a credible source to be frequently cited in their AI‑generated answers.
Some SEO fundamentals remain essential and also strengthen AI Search Optimization (AISO). The two are not in contradiction. It’s not “either or”. Optimizing for AISO, though, requires some additional measures, considering the fact that AI search results are generated differently than traditional SERPs.
What is retrieval‑augmented generation (RAG)?
Retrieval‑Augmented Generation (RAG) is an AI architecture that combines information retrieval with large language model (LLM) generation to produce more accurate, up‑to‑date, and answers backed by relevant sources.
Instead of relying only on what the model has memorized during training, RAG allows the model to search for relevant documents in real time, pull them in, and use them as context before generating a response.
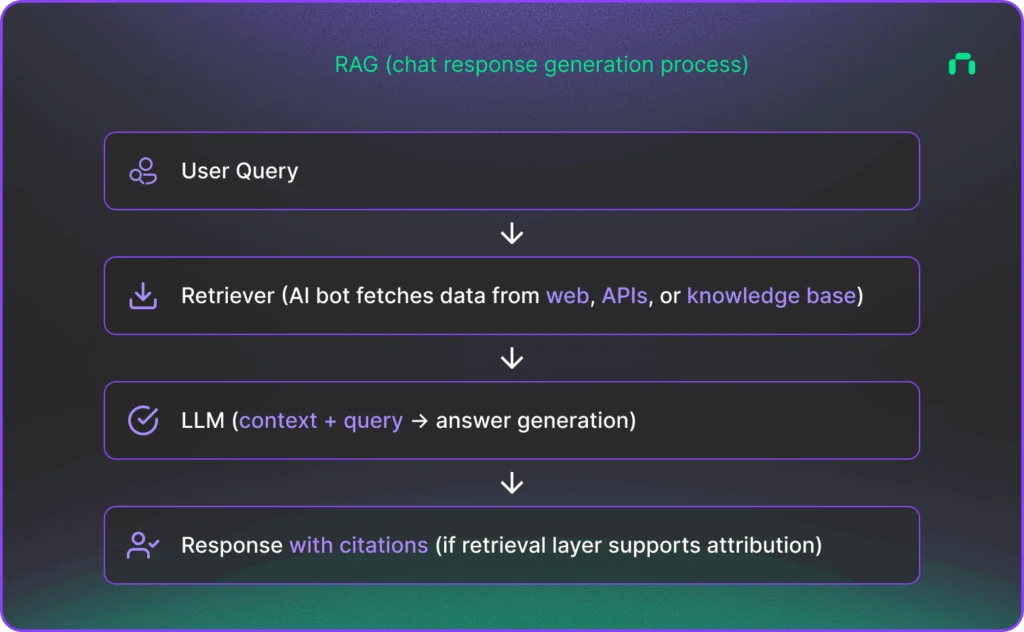
That’s what makes a huge difference between how traditional SEO and AI Search Optimization work.
The technical difference between classic SEO and AI Search Optimization (AISO)
AI is no longer “static” like traditional search
- SEO in its traditional form was built for search engines indexing cached copies of web pages.
- LLMs increasingly fetch data in real time or from retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) pipelines, where the model queries external sources (APIs, live pages, or prebuilt knowledge bases) before generating a response.
That’s why technical accessibility (e.g., crawl permissions, structured data, page speed) directly impacts whether your site even gets pulled into that retrieval step.
Citation requires machine‑readable structure
If your site is crawlable but lacks structured, chunked, and metadata‑rich content, LLMs may retrieve information from your site without necessarily attributing it if the content lacks clear structure or metadata. Or, they may prefer competitors’ sites that are easier to parse and validate.
RAG systems tend to rank sources based on clarity, confidence, and retrievability, not just textual relevance.
Emerging LLM bots behave differently from Googlebot
Tools like Perplexity and OpenAI’s browsing bot often respect robots.txt file, but they also:
- Evaluate JSON‑LD and llms.txt files.
- Prioritize “FAQ-like” or “chunked” answers over long-form pages.
- Skip heavy, JavaScript-rendered pages if they can’t easily extract content.
Without technical readiness, your site may be “invisible” to these newer retrieval layers even if it ranks well in Google.
Direct AI traffic bypasses Google SERPs
As more queries get answered inside AI platforms (zero-click queries), the only way to be cited or linked is by ensuring your site can be fetched and interpreted by LLM pipelines.
This makes it a technical issue (crawl speed, metadata, structured data, API endpoints, etc.), not just a content-writing challenge.
The technical areas of optimization for improved AI Search Visibility
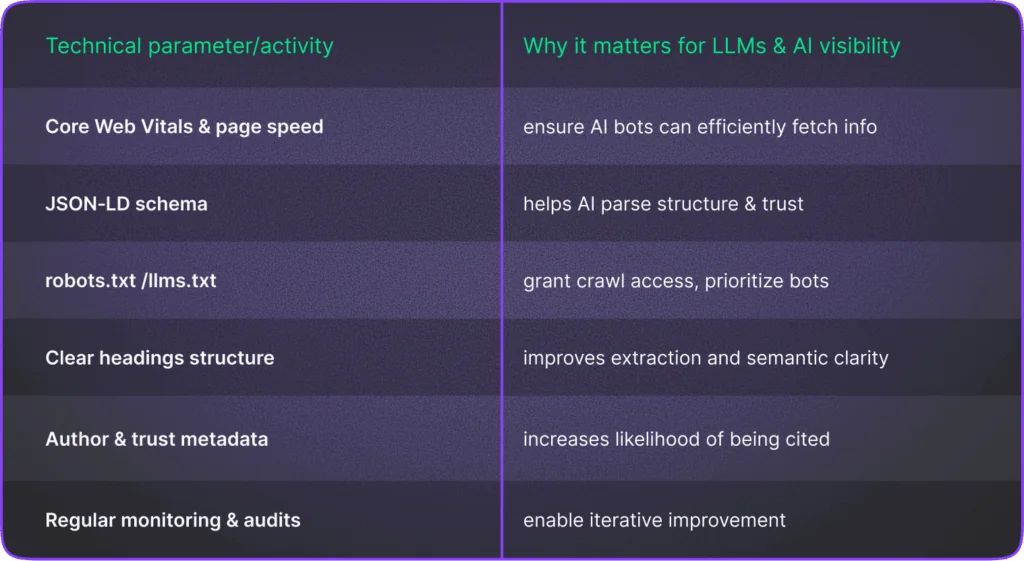
1. Page performance & Core Web Vitals
Fast page loading and responsiveness matter just as much, if not more, than in case of classic SEO, because LLM tools often simulate crawl behavior and skip heavy or slow pages.
- Aim for Core Web Vitals thresholds:
LCP < 2.5 s
INP < 200 ms
CLS < 0.1
Those are the values recommended by Google in Core Web Vitals – but why do they matter for AI retrieval, not just for SEO?
Even though LLMs like ChatGPT or Perplexity don’t “see” your Core Web Vitals scores directly, these metrics indirectly affect whether retrieval bots can fetch, parse, and use your site.
Fast loading (LCP) plays a crucial role because AI crawlers often have strict timeouts. If your site is slow, it might not be fully processed. Low INP and CLS stand for clean and stable rendering, which improves DOM extraction for headless browsers used by LLM browsing tools.
Sites that perform well on these metrics are usually well-structured, less dependent on client-side JavaScript, and easier for machine parsing.
Additionally, Perplexity and other RAG pipelines likely favor pages that render quickly and cleanly because they’re easier to convert into text chunks.
- Use image compression, browser caching, CDNs, and mobile‑first responsive design.
These optimizations matter because they make your site faster, easier to load, and easier for AI bots (and humans) to process. Many AI tools (like ChatGPT browsing) won’t wait long for heavy assets to load – that’s why image compression matters.
AI systems often fetch multiple pages from the same site, so caching speeds up repeat requests, which increases the chance your content is fully retrieved and parsed.
Content Delivery Networks (CDNs) distribute the site’s files across servers worldwide so they load from the nearest location. Why does it matter? AI crawlers and RAG pipelines may run from various regions. A CDN ensures global low-latency access, reducing the risk of your page being skipped because of slow load times. CDNs also often handle compression and caching automatically.
And last, but not least, mobile-first design plays a crucial role here as well, since many AI bots use mobile-like rendering when crawling. If your site breaks or hides content on mobile view, AI retrieval systems may miss important sections.
2. Bot access & crawlability
- Make sure that robots.txt and LLMs.txt files permit AI bots to index your pages – some emerging platforms support dedicated llms.txt files listing priority URLs (more about LLMs.txt later in this article).
- Make your website accessible for crawlers like GPTBot, ClaudeBot, or Google-Extended. Avoid unintentionally blocking AI crawlers due to misconfigured CDN, crawler user agents, or robots directives.
Your website should be accessible not just for humans, but also for bots, if you want your brand to be present in AI-generated recommendations.
Important note: Pages hosted on Cloudflare may block access to AI crawlers. After July 1,2025, upon sign-up with Cloudflare, every new domain will be asked to explicitly allow or deny AI crawlers access. So if your website is based on Cloudflare and you aim at AI Search Optimization – make sure to have that checked and unlocked.
- Maintain and update XML‑sitemap entries regularly so bots can discover new content.
An updated XML sitemap is like a directory of all your important pages, which helps AI bots avoid missing new or deep pages that aren’t well-linked internally. RAG systems prioritize fresh, relevant content, so if your sitemap is stale or incomplete, bots may not find your newest posts or updates in time to surface them in AI-generated answers.
3. Structured data
Structured data plays a significant role in AI Search Optimization. Instead of depending only on the raw HTML, LLMs look at structured data to understand what a page represents: whether it’s an expert-written article, a product page with reviews, or a concise answer to a specific question.
- Implement JSON‑LD schema (e.g. FAQPage, HowTo, Organization, Person) to help AI systems parse page structure and attribution metadata.
4. Semantic clarity & chunking
Structuring content into clearly labeled chunks (QA pairs, bullet lists, short paragraphs) increases “readability” to LLMs. It’s what we refer to as LLM readability & chunk relevance – that’s what needs to be taken care of on the content side.
On the technical side:
- Use an ordered headings structure H1/H2/H3, to help AI bots understand, segment, and retrieve your content more accurately.
5. Bot‑oriented file signals (llms.txt)
- Deploy LLMs.txt as a guide for AI crawlers to high‑priority pages. That’s an emerging best practice, still in testing.
LLMs.txt file parallels robots.txt, but specifically for LLM retrieval bots. It’s not a standard yet, but implementation does not require a lot of time and effort, and does not affect traditional SEO in any way. An internal research by Insightland shows that after implementing LLMs.txt, the number of visits from AI-powered chats increased significantly in a very short period.
6. Trust signals & AI attribution metadata
AI retrieval systems and LLMs increasingly look for machine-detectable trust signals to decide which pages to cite. Chats are more likely to trust and cite content that: comes from identified, credible experts rather than anonymous pages and is fresh and up-to-date. To help LLMs decide your content is worth citing, follow these steps:
- Publish clear author bios, organizational data, publication dates, and versioning to reinforce credibility and trust, which LLMs weigh for citations.
- Mark up this information with schema (e.g., Author, Organization, datePublished and dateModified) to help LLMs confirm your site is legitimate and authoritative.
- Use versioning, by including “last updated” notes (especially for technical content), to show that your content is actively maintained, and reduce the risk of it being seen as outdated or inaccurate.
7. Monitoring & technical audit tools
Optimization for improved AI search visibility should not be seen as a one-time event, but an ongoing process. There’s some technical housekeeping to do, to make sure AI bots, retrieval pipelines, and LLM-based tools can access, understand, and prioritize your content.
That translates into performing regular crawlability audits, structured data validation, speed and Core Web Vitals monitoring, and llms.txt parser checking.
- Test whether bots can fully access your site (e.g. using Google Search Console)
- Check if your schema markup (e.g., Article, FAQ, Product, Organization) is error-free using tools like Google’s Rich Results Test or Schema.org validators.
- Track the performance metrics previously discussed in this article (LCP, INP, CLS) with tools like PageSpeed Insights.
- Review and test your LLMs.txt file if you use it (we can help with that).
- Track changes in Google Search Central guidance and AI‑feature developments to stay technically compliant.
Summary of technical measures for AI Search Optimization
Conclusion
AI Search is rapidly reshaping how information is discovered, cited, and trusted online. Though traditional SEO fundamentals remain relevant, they are no longer sufficient on their own. If you want to be where your customers are, your website must be technically prepared for AI‑driven retrieval to boost the likelihood of citation in AI-generated answers.
On top of deep, properly edited content, parameters – like page speed, structured data, schema markup, proper implementation of robots.txt & LLMs.txt – ensure that LLM‑powered tools such as ChatGPT, Perplexity, or Gemini can not only access your content but also interpret it with confidence and attribute it correctly.
The shift from keyword‑based rankings to machine‑readable, retrieval‑ready content should be seen as a new business opportunity. Companies that proactively adopt AI Search Optimization (AISO) practices will position themselves ahead of the curve, building visibility directly within AI platforms where customers increasingly search.
By treating AISO as an ongoing, measurable process – supported by regular technical audits – you can optimize your website not only to be indexed in traditional SERPs, but also chosen and cited as a reliable source in the AI-generated answers and recommendations.